
04 Feb Best Practices in Food Security: Building Resilience Through Innovation
In a world where around 733 million people still face hunger, food security has become one of the most pressing global challenges of our time. However, innovative solutions are emerging to address this complex issue, offering hope for a future where hunger and resource scarcity are significantly reduced, or maybe even eradicated. From advanced agricultural technologies to more sustainable supply chains, breakthroughs in food security are making a tangible impact.
While the statistics are daunting, technological and social innovations provide new pathways toward achieving Zero Hunger, one of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for 2030. Here are some of the most promising breakthroughs.
- AeroFarms
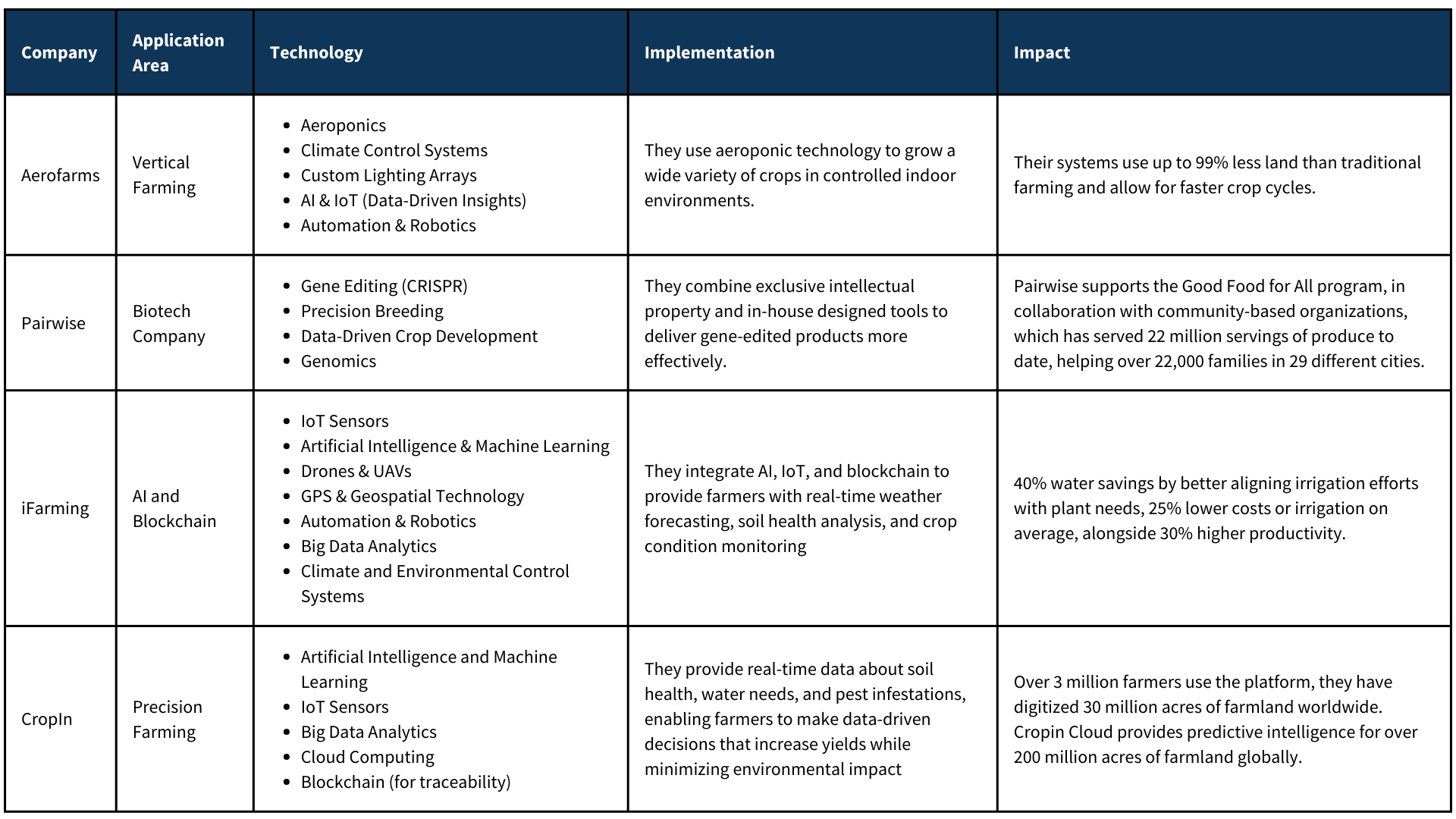
Urban areas worldwide are expanding rapidly, but the space to grow food within these crowded cities is limited. Vertical farming drastically reduces the need for arable land and can be done in urban environments, making it possible to grow fresh produce closer to consumers, and reducing transportation costs and food waste. AeroFarms is a leading company in the field that uses aeroponic technology to grow a wide variety of crops in controlled indoor environments. Their systems use up to 99% less land than traditional farming and allow for faster crop cycles. AeroFarms’ business model addresses 12 of the 17 United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals and is a recipient of the inaugural Global SDG Awards celebrating private-sector leadership in the advancement of the United Nations 2030 Agenda.
- Pairwise
The looming threat of climate change continues to undermine food security, with droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures increasingly affecting global crop yields. Pairwise, is a biotechnology company, founded by a team of experts that uses CRISPR and gene editing techniques to transform plants and the production systems that are built upon them. They combine exclusive intellectual property and in-house designed tools to deliver gene-edited products faster and more effectively. Pairwise uses gene editing to improve the nutrition and yield of crops such as strawberries and lettuce, ensuring that they are not only more resistant to climate change but also more nutritious, potentially tackling malnutrition at the same time.
- iFarming
IBM’s iFarming supported by IBM Watson Decision Platform for Agriculture integrates AI, IoT, and blockchain to provide farmers with real-time weather forecasting, soil health analysis, and crop condition monitoring. The platform uses data from multiple sources, including weather patterns, satellite imagery, and sensors, to deliver actionable insights and understand critical factors such as soil temperature and moisture levels, crop stress, pest and disease risk and identification, yield predictions, and alerts. That helps inform decisions like irrigation, planting, fertilization, worker safety, trading, and pest and disease eradication. Their technology has resulted in 40% water savings by better aligning irrigation efforts with plant needs, 25% lower costs or irrigation on average, alongside 30% higher productivity.
- CropIn
Precision Farming technology provides real-time data about soil health, water needs, and pest infestations, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions that increase yields while minimizing environmental impact. In India, AI company CropIn Technology has been leveraging AI to support precision farming. They provide real-time insights on crop health, soil conditions, and weather predictions. With over 3 million farmers using the platform, Cropin has digitized 30 million acres of farmland, positively impacting over 7 million farmers worldwide. Their crop knowledge graph, spanning 350 crops and 10,000 varieties in 103 countries, powers the Cropin Cloud in providing predictive intelligence for over 200 million acres of farmland globally. Cropin is at the forefront of uniting agribusinesses, development agencies, international organizations, and governments to leverage Agtech systems to transform global food systems and attain climate goals.
Moving Toward Zero Food Insecurity
While the global hunger crisis remains urgent, these technologies have the potential to transform how food is produced, distributed, and consumed. By continuing to scale up these innovations, we can reduce the number of hungry people worldwide and address the scarcity of resources that exacerbates food insecurity.
The road to Zero Hunger might still be long, but at Frost and Sullivan Institute, we believe that it is within reach with the combined efforts of governments, businesses, and innovators. As these technologies evolve, and as investment in food security continues to grow, the goal of feeding the world sustainably and equitably is moving closer to reality. Ultimately, the question isn’t whether we can innovate our way out of food insecurity but how quickly we can implement these solutions to ensure that everyone, everywhere, has access to sufficient, nutritious food.
Blog by Shreya Ghimire,
Research Analyst, Frost & Sullivan Institute


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.